VeradiVerdict - Facebook Launches Libra Token, What Does This Mean? - Issue #43

Hi, I am Paul Veradittakit, a Partner at Pantera Capital, one of the oldest and largest institutional investors focused on investing into blockchain companies and cryptocurrencies. The firm invests in equity, pre-sales/IEO rounds, and active trading of cryptocurrencies on the secondary markets. I focus on early investments and want to share my thoughts and what’s going on in the industry in this weekly newsletter. If you ever come across, or have an interesting project that you would like to share, please reply to this e-mail!
View this issue on my Medium blog here.
If you aren’t subscribed already, you can click here to subscribe.
Please fill out a NEW survey by clicking here
Editorials
Facebook, the world’s largest social network, announced the launch of their blockchain project Libra which sent ripples throughout our industry. I wrote in the past about my thoughts on what the company might launch but more details including a whitepaper was released last week. Below you can read more details on what was announced and thoughts on what this could mean.
TL;DR:
• Facebook recently announced the launch of Libra, a new decentralized cryptocurrency, and Calibra, a Libra wallet that integrates with Facebook’s core products (Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp), as part of their mission to connect the world through better financial accessibility.
• Libra uses a public, open-source blockchain that uses proof-of-stake and a modified version of Byzantine Fault Tolerance (called LibraBFT) that has leaders propose and validate blocks to advance consensus on the network. It also supports smart contracts through their new programming language called Move.
• The goal for Libra is to have low-volatility, which is why it’s backed by a Libra Reserve that currently consists of the US Dollar, British Pound, Japanese Yen, and Euro. The Reserve will diversify its currencies in the future by adding more uncorrelated currencies.
• Libra is governed by a Libra Association, a network of 100 organizations from a plethora of industries that have the power to control the Libra blockchain. Right now, there are almost 30 committed members including Visa, a16z, and MasterCard. More organizations will join over the next few months as long as they comply with Libra’s requirements of size and operations. Libra offers a Libra Investment Token (LIT), $10M worth of which is required to govern the Libra blockchain. This means Libra is starting as permissioned, but will transition to permission-less in the future.
• Calibra operates as a money-services business as a subsidiary of Facebook, but claims not to share any data with Facebook. Calibra is Facebook’s user-facing side of Libra.
• Facebook hopes to increase financial access through Libra and Calibra, particularly for the 1.7 billion individuals worldwide that aren’t banked. Facebook’s ubiquity and scale makes this a real possibility; its size dwarfs any other electronic banking system, which means easy Facebook integration is a promising path for deploying Libra to common users.
• Simultaneously, Facebook continues to receive flack for questionable practices regarding privacy and data sharing. The US Senate has even scheduled a hearing on Libra in mid-July to discuss its compliance with US and global regulations.

Last week, Facebook formally announced the launch of their new decentralized cryptocurrency Libra and their corresponding Facebook product, a wallet for Libra called Calibra. To say the least, Libra flooded the headlines of just about every tech circle (not just cryptocurrency) and has been at the top of everyone’s minds. Having a behemoth like Facebook commit to the decentralized financial future through their own cryptocurrency means a lot for the blockchain community.
How does it all work, technically?
Libra is built on an open-source, public blockchain called the Libra Blockchain that integrates some of the common developments we’ve seen in blockchain innovation over the past few years. The Libra Blockchain is completely new and native to Libra, unlike other corporate cryptocurrencies (e.g. JP Morgan’s) that run on forks of Ethereum or other, more established blockchains. Everything is pseudonymous (like Bitcoin) and governed on-chain.
Libra uses a proof-of-stake (PoS) protocol, like Ethereum, where the creator of the next block is chosen by an algorithm that optimizes for how long or how much value a user has in the network (formally known as their stake). PoS is becoming the new standard for cryptocurrency consensus protocols because of its high security, low latency, and inherent propagation of value in the network because it benefits those who have the most value and ownership of the network.
Within PoS, Libra uses a modified version of the Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) consensus algorithm called LibraBFT. At a high level, BFT is essentially a cryptographic and probabilistic method for determining consensus even when it’s suspected that certain nodes of a network might be corrupted (technically called Byzantine nodes). Libra takes the vanilla BFT algorithm and adds their own customizations and modifications to natively integrate it with their blockchain architecture.
Essentially, the LibraBFT algorithm randomly chooses a leader out of all of the network validators to propose a new block; once the new block is proposed, the other validators must approve the block by majority before the block is sent to a new validator. If the block is not approved or if the leader cannot propose a block, a new validator is chosen as the leader. LibraBFT helps guarantee the safety of the blockchain, allows for asynchrony or disagreement between the nodes, and ensures finality of all transactions. It’s a fairly advanced, fast, and highly-trustable consensus algorithm reflecting a ton of the recent innovations in consensus protocols over the past few years.
Financially, Libra is not a stablecoin (meaning its value is not pegged to any one asset/fiat currency in particular), but it is backed by low-volatility assets in an account called the Libra Reserve. Currently, the reserve consists of the US Dollar, the British Pound, the Japanese Yen, and the Euro. The Reserve eventually hopes to expand beyond just those four currencies––their criteria for adding new currencies include quotability, a public decision-making process, and non-correlation from other currencies and assets. The idea here is to keep the value of Libra relatively stable by backing it with fiat, but not pegging the value of Libra to any one fiat currency in particular. This aims to assert Libra’s value as a stable, usable currency, but not totally lose its decentralization by completely tying it to a government-regulated asset.
On top of the core cryptocurrency side of things, Libra also supports smart contracts (including out-of-the-box contracts that developers can just deploy instead of writing it themselves). This allows for incredible degrees of abstraction for developers that aim to use Libra to support decentralized apps and other decentralized tools to help advance Facebook’s new notion of a global, decentralized financial ecosystem. The smart contracts must be written in Move, a newly-developed programming language optimized for Libra smart contracts and LibraBFT.
How is Libra regulated and governed?
Here’s where things get even more interesting. Facebook totally understands that they, a highly centralized company, and trying to launch a completely decentralized product. To get around that, they’ve helped set up a non-profit called the Libra Association.
The Association will initially consist of 100 members or validators of the Libra blockchain. There are currently around 30 committed founding members, like Visa, Andreesen Horowitz, and Coinbase; Facebook is inviting more from a diverse selection of industries (telecommunications, blockchain, venture capital, academia, etc.) to join the Association over the next few months before it formally launches the Libra blockchain.
Validators are required to host their own node and also meet a couple of criteria, including: (1) having $1 billion+ in market value, (2) reaching 20 million+ people a year, and (3) be recognized as a top-100 industry leader by a reputable third party (like the Fortune 500). There’s some flexibility on these requirements when it comes to social institutions, non-profits, and academic universities that may not have all these requirements down, but still provide immense value to Libra’s governance.
Libra also uses a two-token system to implement governance. Libra offers a token called the Libra Investment Token (LIT) which allows validators to govern the network. Validators must hold minimum $10M value in LIT to regulate the network; again, these requirements are more relaxed for social institutions, non-profits, and academia. This is similar to what MakerDao does with Maker (their governance token) and Dai (their stablecoin).
So, you’re saying Libra isn’t really open to the public yet?
Exactly. Libra is starting out as permissioned, which means the association regulates which organizations and parties have permission to regulate the network and the blockchain. Facebook understands that this fundamentally prevents Libra from being 100% decentralized, but it claims that the permissioned nature of Libra is only a temporary way to allow Libra to test itself and help identify kinks and bugs in the protocols for governance. Once this has all been worked out through repeated testing and usage of the testnet, Libra plans to transition to a permission-less system to make it openly accessible.
What is all this Calibra business?
Calibra was established as a subsidiary of Facebook to integrate Libra into Facebook’s products as a financial tool. Recall that Libra isn’t technically directly governed by Facebook, but rather by an association of 100 organizations (which include Facebook). To get around this, Facebook established Calibra as a technical business where they can create Libra wallets that easily integrate into Facebook’s key products (Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp) and allow for Libra payments to occur over these social media and messaging channels.
Calibra is also how Facebook purportedly complies with governmental regulations. Compliance is a mess for just about any cryptocurrency, and Libra is no different, because different governments have different requirements that allow for different degrees of collateralization, privacy, transaction volumes, taxing, etc. Calibra is set up as a money-services business, collaborating with FinCEN (Financial Crimes Enforcement Network) to ensure Facebook’s decentralized business complies with all US regulations. Facebook also claims that there will be absolutely no data-sharing between Calibra and Facebook’s core business aside from what’s federally required. Despite these measures towards compliance, there’s likely more regulatory road bumps that Facebook and Calibra will face, like GDPR.
Put simply, Calibra is the product side of Facebook’s decentralized developments. It’s how they make money from Libra.
Facebook’s never been in the blockchain business. Who on their team is running it?
The entire initiative for Libra and Calibra is run by David Marcus, the current VP of Blockchain at Facebook. Prior to that role, David headed Facebook Messenger, was on the Board of Directors at Coinbase, was the president of PayPal, and created a mobile payment company (Zong) that he sold to PayPal. The rest of the team comes from diverse backgrounds, including product, strategy, and investing roles at Messenger, Instagram, Yahoo, eBay, and McKinsey & Company. The team’s collective knowledge spans multiple domains of mobile payments, blockchain, communications, and consumer services.
Why does this all matter so much? Why can’t people stop talking about it?
Facebook’s entire mission as a company is to connect the world. There are currently 1.7 billion individuals globally that are unbanked and don’t have great access to even basic financial resources; financial transactions are one of the most fundamental ways that people connect with each other.
Libra and Calibra help advance Facebook’s mission to connect all these people. There’s no need for a full-fledged bank for the unbanked 1.7 billion if they can just run all their transactions and manage their funds through Libra and Calibra, tied to their Facebook account. The idea is to promote the global decentralized economic system and guarantee financial access to anyone who can access the Internet. Being a cryptocurrency, Libra also presents more opportunities for arbitrage and optimized trading strategies.
What’s even more critical is Facebook’s size and genuine potential to accomplish this mission. Facebook has 2.7 billion users worldwide; to give you an idea for scale, WeChat has 1.1 billion, PayPal has 0.3 billion, Venmo has 0.04 billion, and Bitcoin has 0.02 billion. If Calibra can easily integrate financial payments into Facebook’s product, the scale of Calibra would instantly dwarf any other electronic banking option. Facebook has already reached such a significant portion of the world that it genuinely has the potential to establish a banking system of scale and provide banking resources to those that need it most.
Facebook’s goal for Libra and Calibra is exceedingly noble, but that doesn’t mean it hasn’t met its fair (and deserved) share of criticism. Facebook isn’t exactly the most trustable company; it’s been in the headlines for a while now with scandals of user privacy leaks, undisclosed data collection, ethically questionable ad-based business models, etc. It’s hard to imagine a company with the reputation of Facebook establish a decentralized, “trustable” financial system. Facebook claims that they will keep Calibra and Facebook completely distinct, and Libra itself is governed by a non-profit, but that doesn’t stop the sentiments of hundreds on Twitter doubting Facebook’s true motives with Libra and their ability to implement a trustable system. Libra also plans to debut in 2020, but the US Senate has already scheduled a hearing for July 16 to discuss Libra and evaluate its compliance with US and global financial regulations and how it interacts with Facebook’s unsettled business with the US government and antitrust regulations.
Final Thoughts
Libra’s a technically strong cryptocurrency that provides a promising solution to the problem of billions of unbanked individuals globally; it’s one of the first steps towards a financial future of decentralization, trust, and most importantly, high accessibility. Its integration of the most advanced and sound blockchain technologies like BFT and two-token systems helps make Libra a decentralized, low-volatility option for financial transactions. And with Facebook’s scale, Libra truly has the potential to reach billions worldwide and become a highly used product through Calibra native integration with Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp accounts.
At the same time, Facebook’s history and reputation opens up a lot of questions for what the future of Libra holds. For starters, it’s launching as a permissioned ecosystem, fundamentally preventing it from achieving its mission of connecting the financial world. Additionally, Facebook’s faced immense flack for poor diligence on user privacy and data collection––to the extent that even the US government is worried about Facebook’s new cryptocurrency.
Altogether, Libra presents a promising, but questionable, foray into a decentralized financial future. The launch of the testnet in 2020 will inevitably create huge waves in the blockchain community and will help expose some of the critical flaws in Libra’s architecture and governance and better inform Libra’s potential as the global financial connector.
Nevertheless, the scale of Facebook enables the possibility of a more decentralized payments network that can enable low-cost remittances and payments over a global low-volatility currency for billions of people (especially for the emerging markets that have a much higher penetration of Facebook users than the United States). As an investor, there would be investment opportunities in companies and applications that build on top of the Libra infrastructure, while for consumers, imagine a global venmo and the ability to make payments without the friction of high fees and different currencies.
Digests
Libra's Dante Disparte on Why We Should Trust a Financial System Designed by Facebook - Ep.078 by Unconfirmed Podcast | Free Listening on SoundCloud
Stream Libra’s Dante Disparte on Why We Should Trust a Financial System Designed by Facebook - Ep.078 by Unconfirmed Podcast from desktop or your mobile device
Facebook releases plan for its Libra cryptocurrency to 'meet the daily financial needs of billions of people' - The Block
Facebook today unveiled its new low-volatility cryptocurrency Libra, powered by a smart contract platform that’s designed to be “secure, scalable, and reliable”
In the Tweets
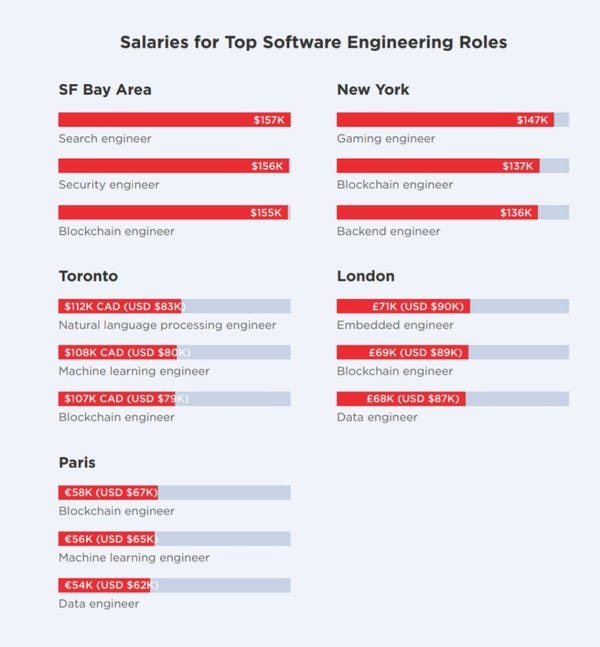
5 out of the top 5 global cities have "Blockchain Engineer" as one of the highest paying (and most sought-after) tech jobs our there.
(Source: @Hired_HQ) https://t.co/vhxGQtvCss
12:03 PM - 20 Jun 2019

THREAD: Here are my thoughts on Libra. It is a permissioned but public blockchain. It’s public because the Blockchain will be publicly verifiable and the application layer is open. So it’s like a backed stablecoin, but with key differences. https://t.co/UZ3fkczWGb
2:08 AM - 18 Jun 2019
News
Algorand Raises $60 Million in Token Sale - CoinDesk
Algorand raised over $60 million in a token sale of its native Algo token on Coinlist, using a Dutch Auction mechanism that ensures market participants set a uniform price per Algo. All 25 million tokens were sold at a market drive price of $2.40.
Crypto Mining Giant Bitmain Said to Be Planning US IPO: Bloomberg - CoinDesk
Crypto mining hardware giant Bitmain Technologies Ltd. is said to be relaunching its initial public offering (IPO) plans, but this time in the U.S. instead of Hong Kong.
Line Said to Near Approval for Japan Crypto Exchange License - Bloomberg
Line Corp., Japan’s largest messaging app, is close to getting a license to launch a cryptocurrency exchange in its home nation, according to people familiar with the matter.
Microsoft and Ethereum Foundation Swell the Hyperledger Ranks Amid Growing Cross-Industry Blockchain Collaboration
Microsoft, the Ethereum Foundation and Salesforce join Hyperledger as new members, seeking to create open-source enterprise blockchain solutions.
Regulations
Halt Libra? US Lawmakers Call for Hearings on Facebook's Crypto - CoinDesk
The head of the U.S. House of Representatives Financial Services Committee wants Facebook to stop developing its new Libra cryptocurrency network – at least temporarily.
Regulators Debate Cryptocurrency Legislation Ahead of G20 Summit - CoinDesk
Cryptocurrency regulation will take a step forward during the upcoming V20 Summit where country representatives will assess the new course of legal action proposed by the international Financial Action Task Force (FATF).
New Products and Hot Deals
Lightning Labs Mobile App Gets 2,000 Downloads in 24 Hours - CoinDesk
San Francisco-based Lightning Labs, focused on a layered scaling solution for bitcoin, released its first mobile app on Wednesday.
Firm Behind Zcash to Introduce New Version of Protocol With Sharding
The Electric Coin Company, the firm behind second-biggest anoncoin zcash, is building a new scalable zcash blockchain.
Meet with Me
Las Vegas, July 12
Los Angeles, July 19
Berlin, Web3 Summit, August 19-21
Los Angeles, August 23
Additional Info
👋 Working on building new technologies? I’d love to hear about it, shoot me an email
🙏 I’d appreciate it if you forwarded this email to someone who would might benefit from it
💡If you have any content you want to share on this newsletter, please send it to me and we can make it happen
Please click here to help me improve this newsletter and your experience by filling out this NEW survey!

