VeradiVerdict - Why Lightning is Bitcoin's Best Hope for Scalability - Issue #27

Hi, I am Paul Veradittakit, a Partner at Pantera Capital, one of the oldest and largest institutional investors focused on investing into blockchain companies and cryptocurrencies. I focus on early stage investments and want to share my thoughts and what’s going on in the industry in this weekly newsletter.
Please click here to help me improve the newsletter and your experience by answering just ONE question!
If you were forwarded this email, you can click here to subscribe.
Editorials
TL;DR
● The current problem with Bitcoin is that transactions are too slow (approximately 10 minutes to confirm, since the system limits to 5-10 transactions per second) and that the transaction fees are too high and unpredictable with spikes in demand. These limit Bitcoin’s potential as a blockchain for new applications and convenient, fast transactions.
● The Lightning Network is a protocol that runs on top of the Bitcoin blockchain to offer a solution to these problems. It uses payment channels, which are all chained together by smart contracts, to run faster, more real-time transactions that are later secured and finalized by the Bitcoin blockchain. It offers infinitely faster speeds, without compromising much of Bitcoin’s original security.
● Since its inception in early 2018, Lightning has grown incredibly––it’s reached 2.8 million USD in network size in spite of its and is becoming one of the most viral trends across the blockchain community to date. Growth is only prospected to increase in the future.
● Since its inception in early 2018, Lightning has grown incredibly––it’s reached 2.8 million USD in network size in spite of the limits they’ve put in place on the amount per channel and per transaction. It’s becoming one of the most viral trends across the blockchain community to date, growth is only prospected to increase in the future once Lightning lifts these limits.
● Some interesting applications of the Lightning Network include: consumer-oriented marketplaces for exchanging digital assets that can process transactions much faster, micropayment systems enabled by Lightning’s low transaction fees, and business-facing tools to help integrate cryptocurrency into electronic payment systems.
The Problem with the Current System
Bitcoin, in its original form, is a highly advanced technology, but not without a few inherent flaws. Bitcoin’s underlying genius is built off of the infamous proof-of-work protocol, which powers the security, consensus, and decentralized nature of the cryptocurrency.
At a high level, the current system requires every computer on the blockchain network to verify every new transaction. Miners help create blocks and secure the network to store more transactions.
The problem with this system is that because of its security parameters, it takes a long time. On average, it takes roughly 10 minutes to confirm a Bitcoin transaction. This creates issues for two main reasons.
First, developers and consumers both don’t want to wait for extremely high transaction speeds. They can make plenty of transactions relatively quickly, but the current infrastructure limits the speed at which transactions can be verified and validated by the system and consensus protocols.
Second, in recent weeks especially, the price of Bitcoin has been becoming increasingly volatile, with fluctuations of even 10 USD in the price within a span of 5 minutes. Between the time when a transaction is initiated and confirmed, the value of that transaction can change pretty drastically. Longer block time makes it harder to limit volatility.
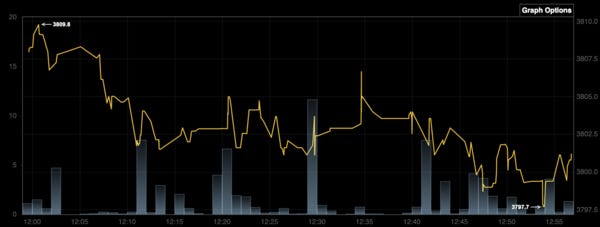
Fig. 1: Fluctuations in the Price of Bitcoin from 12pm-1pm PST on 3/2/19 from BitcoinTicker.Co
Additionally, the fees collected by Bitcoin range between 5 to 15 cents per transaction––meaning micropayments, a huge possible market for cryptocurrencies, are essentially impossible.
What is the Lightning Network?
The Lightning Network is a second-layer network that helps power faster, more efficient transactions that make things a lot easier for the average Bitcoin user or developer. Essentially, Lightning runs on top of the Bitcoin blockchain to do its job; it acts in between those that need to interface with the Bitcoin blockchain (developers, people making transactions, etc.) and the actual blockchain itself. With its infrastructure, it offers much faster speeds (less than a second versus 10 minutes by Bitcoin) to developers and consumers without really compromising the security and consensus protocols of the actual Bitcoin network.
How does it work? What does the tech look like?
Lightning operates using a combination of smart contracts and payment channels. Payment channels are essentially a way for two parties to transact money without operating directly on the blockchain.
When two parties want to exchange money through Lightning, the protocol sets up a multi-signature payment channel between them where each party has a private key that gives them access to their funds in the channel. When one party wants to send funds to the other, they each sign off on a new state, invalidating the prior state ––but that transaction isn’t reflected on the blockchain, yet. Lightning uses P2P communication between the parties to exchange the funds, and the transaction is history is recorded on each party’s node as a “redeemable receipt”––consensus is temporarily implemented by just those two nodes, rather than the entire blockchain network. Once one or both of the parties want to move their funds back to the blockchain, the protocol then updates the blockchain to reflect the final state.
But Lightning’s benefits aren’t limited to just two parties; Lightning uses peer-to-peer to link multiple payment channels through smart contracts. If person A and person B have a payment channel, and person B and person C have a payment channel, and person A wants to send funds to person C, Lightning powers that transaction by having person A send funds through person B, in a network of payment channels that is completely operated by smart contracts. This lends Lightning lightning-fast speeds across its entire network––not just individual payment channels.\
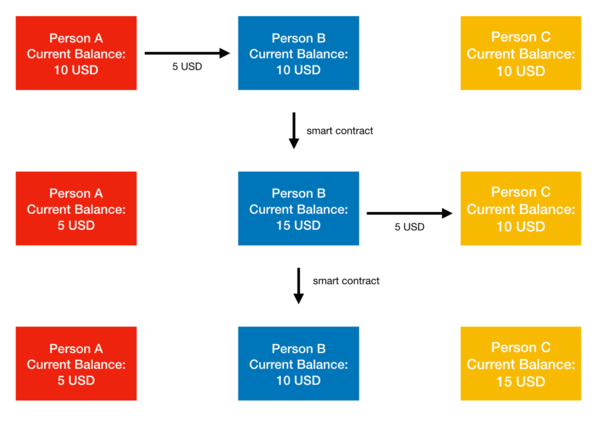
Fig. 2: Smart networks and payment channels. Person A and Person B have a payment channel. Person B and person C have a payment channel. Person A pays person C through a transaction that runs through person B, which is completely implemented by Lightning smart contracts.
Looking forward, Lightning still has a lot of infrastructure work to do before it can completely dominate the Bitcoin market. Lightning currently restricts to 0.1677 BTC per channel and 0.42 BTC per transaction, which limits the total growth of the network. We expect the channel limits to be lifted later this year, allowing the network capacity to grow even further.
What about security?
Because Lightning’s transactions still operate on top of the Bitcoin blockchain, at some point, they will be verified by the entire network through the traditional proof-of-work protocol––just not necessarily immediately at transaction time. But still, there might be security concerns. Let’s say person A and person B have a payment channel, and finally agree to stop transactions––meaning, they want their transactions to be reflected on the blockchain. But what if person A attempts to corrupt their transaction history and instead sends an old transaction to the blockchain to indicate they have more funds remaining then they actually do?
Lightning’s protocols still verify the transaction history between the two parties in the payment channel. When a user on Lightning closes a channel to get funds back on the blockchain the protocol will detect that person A’s outdated history doesn’t match person B’s correct history, and they’ll look out for old transactions specifically to ensure that the histories match up precisely. Once they detect that person A has corrupted the history, a smart contract rescinds all of person A’s funds to person B as a penalty for tampering with the transaction. Lightning’s security essentially operates with local consensus between trading parties, only to later secure it with global consensus.
What about other efficiency-related solutions?
The two other most popular protocols to improve Bitcoin speed are MimbleWimble and Segregated Witness.
MimbleWimble essentially uses additional hashing and encryption between the two parties making a transaction to allow the transaction funds to be spent even before the transaction has been confirmed globally. The major problem with MimbleWimble is that its infrastructure essentially requires blockchainers to fork the blockchain into a sidechain for MimbleWimble transactions––something the community doesn’t see happening anytime soon.
Segregated Witness (SegWit) works on the blockchain itself, by separating signatures and decreasing the size of a transaction, allowing a given block to store more transactions as a result. SegWit enabled Lightning to perform certain smart contract functionalities on the Bitcoin blockchain that are critical to Lightning’s infrastructure. One of its main goals was to enable Lightning, and it works incredibly well in conjunction with the protocol.
Aside from these two major developments, the next most popular option is to just interact with the Bitcoin ecosystem directly––again, this leads to issues like poor transaction time unpredictable fees that can spike that have limited Bitcoin’s growth in a variety of spaces. Lightning effectively removes these barriers, making it a lot easier for developers to create new applications with Bitcoin and makes the whole transaction process a lot more convenient.
How’s it been doing, numbers-wise?
Lightning debuted on bitcoin’s mainnet at the beginning of 2018, and ever since, it’s experienced huge growth in usability and development. Between November 2018 and December 2018, its network capacity nearly quadrupled––all despite the intense bear market, falling prices for Bitcoin, and the network limits that were put in place.

Fig. 3: Number of nodes on the Lightning Network over time. Blue shows nodes currently involved in a payment channel, orange shows nodes not in a payment channel from BitcoinVisuals.

Fig. 4: Total network capacity of Lightning over time from BitcoinVisuals. Blue shows value in USD, orange shows value in BTC.
Even still, Lightning continues to grow. Since its inception, it’s reached 6,906 nodes, 31,180 channels, and 733.89 BTC (2.8 million USD) in total network capacity in this time. Last month alone (February 2019), Lightning’s network capacity shot up 29% and its number of nodes shot up 22%––an incredibly promising and consistent trend for the beginning of 2019.
On the developer side, it’s not doing too shabby either. There are three main implementations for the Lightning Network, lnd created by Lightning Labs, c-lightning by Blockstream, and Eclair by Acinq. Hundreds of developers have already contributed to these projects, and lnd is the most popular with over 170 developers contributing to their open source repository. Further, developers have already built hundreds of apps, tools, and services on the Lightning protocol.
What are the various use cases?
Lightning brings in the payment and value layer to Bitcoin applications, which creates a lot more opportunity for Bitcoin developers who need faster transaction speeds and communication to bring instant, high volume, low fee transactions to their apps, which any on-chain dapp (like EOS or ETH) can’t do.
Because of Lightning’s faster speeds, developers now have the potential to build more apps on the Bitcoin blockchain––conveniently, called Lapps (Lightning apps). Here are some of the more popular Lapps being built:
1. CoinMall: Think of this as a decentralized eBay or Amazon built on the blockchain. It’s an electronic marketplace where users can sell and buy digital assets (like game memberships, music, art, etc.) using Bitcoin and cryptocurrency. It uses Lightning to power electronic transactions with the same speed and convenience that services like Amazon can provide, while maintaining privacy and neutrality in their dealings.
2. OpenNode: Recently, the electronic financial tool Stripe became insanely popular as a convenient platform for small businesses to run electronic transactions with consumers. OpenNode is incredibly similar. It’s an API that interfaces with the Lightning Network that makes it incredibly feasible, easy, and fast for small businesses to transact with customers––on the Bitcoin blockchain.
3. Lightning Joule: This is a browser extension that helps anyone interface with apps that use Bitcoin systems (games, article payments, financial tech, etc.) through the Lightning protocol. It brings the power of fast, low-fee transactions to a myriad of applications.
4. Tippin: With Lightning’s faster infrastructure comes much smaller transaction fees. OnLightning, users pay fractions of a cent per transaction, in comparison to the 5 to 15 cents that Bitcoin charges on average. This means, for the first time ever, Bitcoin can sustain a micropayment system without consuming too much of the payment for transaction fees. Tippin is one of the newest, most popular micropayment systems on Lightning which allows users to make micropayments at insanely low transaction fees. It gets its name from its largest use case––tipping. It launched a Twitter plugin where users could tip directly through Twitter, which became isnanely popular
5. A few other honorable mentions to check out: Yalls.org (Article Micropayments), Satoshis Games (In Game Payments and Tournaments), Lightning Pizza (literally, buy Pizza with Lightning and Bitcoin), PolloFeed.com (feed chickens with Lightning and Bitcoin).
Final Thoughts
Bitcoin has exploded in popularity over the past few years––the blockchain and cryptocurrency revolution is well underway, but the genius of consensus algorithms and security protocols like proof-of-work and ECDSA aren’t enough to carry the revolution through. The Lightning Network is an immensely useful tool for Bitcoin users and developers alike, that helps power faster, more frequent transactions and new uses of the Bitcoin blockchain that couldn’t be realized before. Through insanely fast transaction speeds, incredibly low transaction fees, and scalability to multiple thousands transactions per second, Lightning too has exploded in popularity––becoming one of the largest growing Bitcoin trends of 2018 and 2019, only to continue dominating the market further. Its technology holds immense potential for the future of consensus protocols and Bitcoin as a tool.
Digests
The five camps of crypto – Casey Caruso – Medium
In 2008 the Bitcoin paper described a world which would allow “online payments to be sent directly from one party to another without going through a financial institution.” People saw this vision and…
Security token offerings aren’t looking much better in 2019 – TechCrunch
An analysis of a year of liquidity and trading data
Long the Bankers! Why Security Tokens Need Trusted Middlemen - CoinDesk
As one of the very first people to tokenize a VC fund when the term “security tokens” almost didn’t exist, and as an early investor in the space, I have a unique point of view into the rapid growth of this ecosystem.
Past, Present, Future: From Co-ops to Cryptonetworks – Andreessen Horowitz
In the Tweets

The @fetch_ai token sale on #Binance Launchpad took 11 minutes and 14 seconds to complete 🏁
Thank you to everyone who participated in the sale. This is just the beginning 🚀 https://t.co/RSp4VMkfx3
6:39 AM - 25 Feb 2019
🧐 Check out the February 2019 Crypto Sentiment Survey. I worked with a prominent crypto angel and we surveyed 91 thought leaders in the crypto space. A few of the highlights are below:
https://t.co/JGnBsDZ13u
11:50 AM - 27 Feb 2019
For my long term view, I see Bitcoin going to at least $100,000 within four years. I think it could even reach $150,000 in that time. Eventually, I believe it could surpass $1,000,000. Where do you see BTC going in the long term?
11:39 AM - 26 Feb 2019
These two are really sharp, worth listening to their thoughts on the most important topics in crypto https://t.co/LvH33ZLIxH
8:39 AM - 27 Feb 2019
. @APompliano is right
JP Morgan is trying to create a privatized overlay money system on top of the Fed's USD https://t.co/vi6ZT3k6Ow
1:14 PM - 2 Mar 2019
News
Kabam and esports veteran Kevin Chou turns to blockchain games with Forte startup | VentureBeat
Kevin Chou has made his mark with Kabam in mobile games and Gen.G in esports. And now he has gathered his crew together for blockchain gaming startup Forte.
New Products and Hot Deals
Blockchain startup Nivaura gets funding from London Stock Exchange Group - The Block
Nivaura, a blockchain fintech, has closed its second seed extension round, raising $20 million across all rounds.
Curv Moves to Shake Up Crypto Storage With Cloud-Based Service, Raises $6.5 Million
Curv raised $6.5 million from Team 8 and crypto giant Digital Currency Group to offer cloud-based crypto custody.
ThunderCore raises $50 million to make a faster, cheaper blockchain platform | VentureBeat
ThunderCore has raised $50 million to build a more nimble, cheaper, and faster blockchain platform. It’s like the foundation for a better Bitcoin.
Casa is dramatically shifting its business, and it's kicking off with two new products - The Block
Casa, the cryptocurrency custody startup that aims to maximize safety and security for its crypto users, announced a “core shift” to its business.
Meet with Me
Los Angeles, March 6
San Diego, April 12
New York, Consensus Conference, May 9-18
Additional Info
👋 Working on building new technologies? I’d love to hear about it, shoot me an email
🙏 I’d appreciate it if you forwarded this email to someone who would might benefit from it
💡If you have any content you want to share on this newsletter, please send it to me and we can make it happen
Please click here to help me improve this newsletter and your experience by answering ONE question!

